Cyber Threat Weekly - #6
First off, Happy New Year, and so it begins… a new start to another year. Got to remember to use 2024 instead of 2023. Let’s begin with Carbanak is back and has been observed in ransomware attacks. Poorly secured Linux SSH servers actively attacked.
A new version of Medusa Stealer is released for Christmas. Stealthy Android malware discovered, downloaded over 327,000 times. Extremely sophisticated iPhone attack chain revealed. Remote code vulnerability in Apache OFBiz being actively exploited.
Massive volumes of PII and compromised data leaked on Christmas Eve. Researchers use chatbots to ‘jailbreak’ other chatbots. New malware loader Rugmi daily detections surge. Microsoft disables App Installer after threat actor abuses.
Since Lumma infostealer announced Google session hijacking via expired authentication cookies, several more infostealers now claim the feature. Palo Alto shares a recap of threat intelligence released from October to December 2023.
Broken Record Alert: Let’s talk about patch prioritization!!!
Known exploited vulnerabilities should be priority #1. You can start with the CISA known exploited vulnerability (KEV) catalog. I’m going to change how I talk about vulnerabilities with proof-of-concept (PoC) code available. The new term will be weaponized PoC code.
Every week we share known exploited vulnerabilities being abused by threat actors. Some of these exploited vulnerabilities are quite old. Diligent patching can prevent threat actors from abusing your organization for their gains.
Patch prioritization matters… A picture says 1,000 words, according to Qualys, in 2023 less than 1% of vulnerabilities were considered high risk:
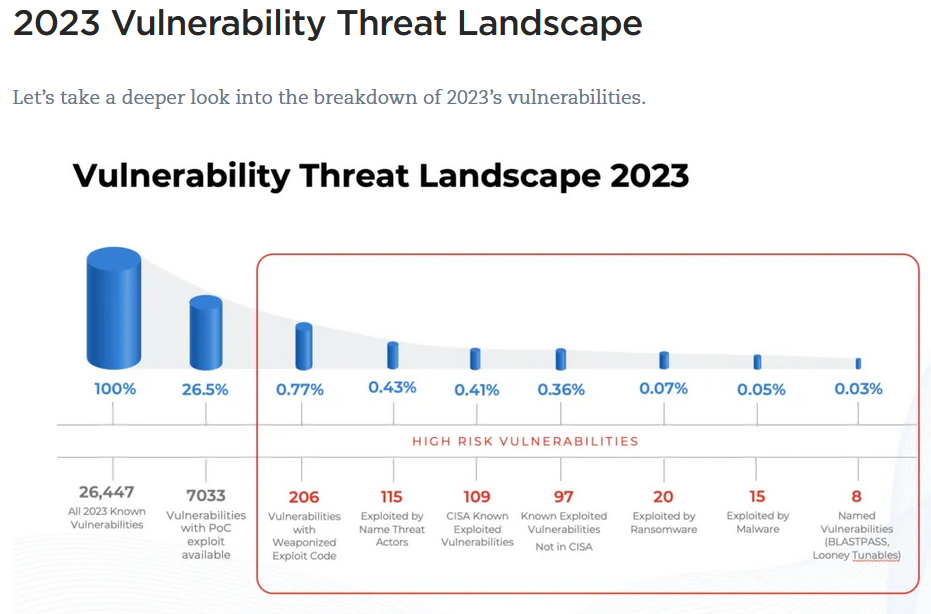
Credit: Qualys
Carbanak Banking Malware Returns
While this comes from a bit older dataset, November 2023, we will be following this trend over time. Carbanak is older, detected around 2014, and has been used by FIN7 in the past. The fact it shows back up in ransomware attacks is interesting.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/carbanak-banking-malware-resurfaces.html
https://www.nccgroup.com/us/newsroom/ncc-group-monthly-threat-pulse-november-2023/
Linux SSH Servers are Targeted by Threat Actors with Dictionary Attack
We, as an industry, need to re-think our external attack surface and what we expose to the Internet. There are better means of remote access such as Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) that minimizes exposed services. This is an example of how threat actors are going after our external attack surface.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/warning-poorly-secured-linux-ssh.html
https://asec.ahnlab.com/en/59972/
Medusa Stealer gets Updated
On Christmas eve, the malware authors released an update to Medusa Stealer malware. With promises of more upgrades to come in 2024.
https://www.resecurity.com/blog/article/new-version-of-medusa-stealer-released-in-dark-web
Android Backdoor Discovered in Numerous Apps
McAfee Mobile research team dubbed the malware Xamalicious, utilizes the Xamarin framework and accessibility permissions.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/new-sneaky-xamalicious-android-malware.html
iPhone Hack Exploitng Hidden Hardware Feature
Kaspersky discovered the campaign in early 2023 after being targeted. The spyware leverages never-before-seen exploits targeting hardware-based security protections in Apple iOS devices. It’s believed this campaign has been ongoing since 2019.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/most-sophisticated-iphone-hack-ever.html
https://securelist.com/operation-triangulation-the-last-hardware-mystery/111669/
Apache OFBiz Remote Code Execution Actively Exploited
Publicly available proof of concept code is being utilized to exploit Apache OFBiz. ShadowServer has detected quite a few sans for the older CVE-2023-49070 which can be bypassed and a new CVE-2023-51467 has been assigned. The fix for the bypass was released December 26th.
https://blog.sonicwall.com/en-us/2023/12/sonicwall-discovers-critical-apache-ofbiz-zero-day-authbiz/
Massive Stolen Dataset Leaked on the Dark Web, ‘Free Leaksmas’
Cybercriminals don’t rest. On Christmas Eve, over 50 million records were shared freely amongst cybercriminals on the dark web.
https://securityaffairs.com/156560/deep-web/leaksmas-dark-web-data-leak.html
Researchers Create a Chatbot to Generate ‘Jail Break’ Prompts
It seems large language models (LLMs) are all the rage. Of course, security researchers work to find the security limits. Creating a chatbot designed to create jail break prompts is interesting and we need to continue to see how LLMs can be attacked and affected by threat actors.
https://techxplore.com/news/2023-12-ai-chatbots-jailbreak.html
Malware Loader Rugmi Usage Rising Rapidly
The massive spike in usage is not good for defenders. Distributing several infostealers after infection, this is one we’ll keep an eye on.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/new-rugmi-malware-loader-surges-with.html
Threat Actors Abusing Microsoft App Installer
Multiple threat actors have used the ms-appinstaller protocol to distribute malware. This activity has been observed since mid-November.
https://thehackernews.com/2023/12/microsoft-disables-msix-app-installer.html
Google OAuth Abuse Allows Account Token Restore
Several infostealers have jumped on the Google account token restore bandwagon. Lumma stealer was the first, at least five more threat actors have announced the feature. This one is worth the read; the sophistication of malware development is not good for defenders.
Palo Alto Threat Intelligence Recap
A write up and threat intelligence shared during Q4 2023 on several malware families. If you have a few minutes, this one is interesting, and provides a timeline of releases from Palo Alto Unit 42.
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/unit42-threat-intelligence-roundup/
31337 InfoSec - Cyber Threat Weekly - Derek Krein Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.
Comments
Sign in to join the conversation.
Just enter your email below to receive a login link.
